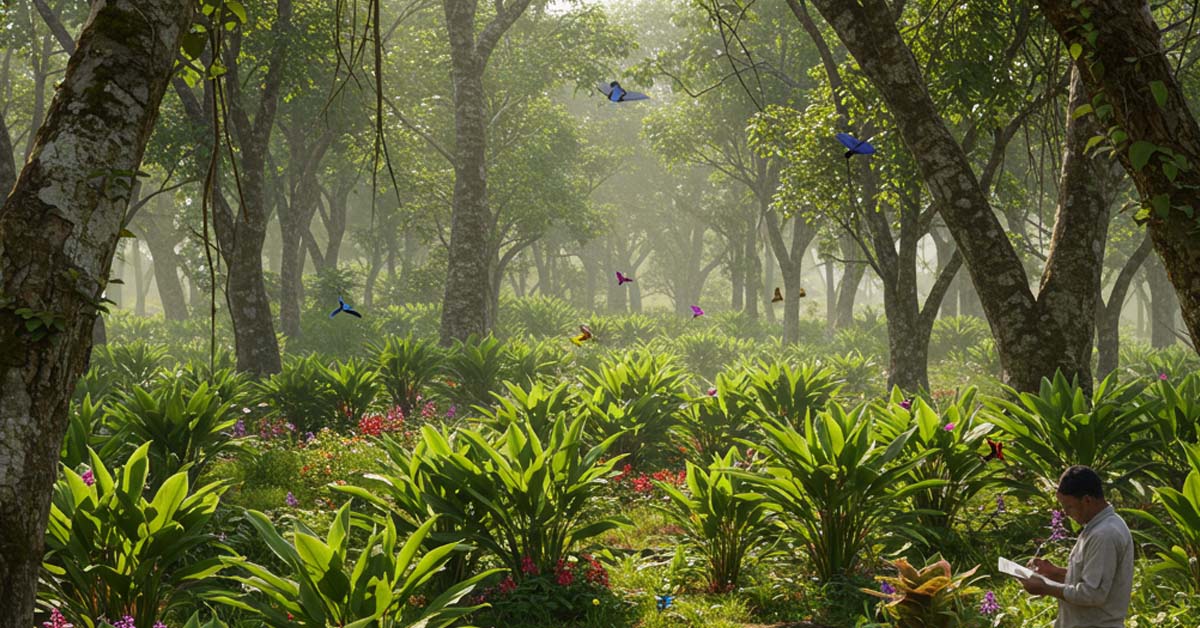
Cardamom is more than just a spice—it plays a crucial role in shaping the ecosystems where it is grown. Depending on farming methods, cardamom cultivation can either support biodiversity or harm natural habitats. Let’s explore the positive and negative impacts of cardamom farming on local biodiversity.
🌱 The Positive Effects of Cardamom Farming on Biodiversity
✅ 1. Shade-Grown Cardamom Preserves Forest Ecosystems
Many cardamom farms, especially in regions like India, Sri Lanka, and Guatemala, use shade-grown methods instead of clearing forests.
✔️ Maintains tree cover, preventing deforestation.
✔️ Creates a habitat for birds, insects, and small mammals.
✔️ Prevents soil erosion by keeping roots intact.
💡 Fun Fact! Shade-grown cardamom plantations act as mini-rainforests, providing shelter for many species! 🌳🦜
✅ 2. Supports Pollinators & Beneficial Insects
Cardamom plants rely on pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and even ants, for reproduction. When cultivated organically, farms encourage:
✔️ Increased pollinator activity, leading to higher biodiversity.
✔️ More natural pest control, reducing the need for harmful pesticides.
✔️ A balanced ecosystem where insects and plants thrive together.
💡 Did You Know? Cardamom flowers attract native bees that help maintain overall plant diversity in forests! 🐝🌸
✅ 3. Promotes Biodiversity Through Agroforestry
Many cardamom farmers use agroforestry techniques, where multiple crops grow alongside cardamom. This:
✔️ Increases plant diversity, making farms more resilient.
✔️ Provides food sources for wildlife and birds.
✔️ Reduces the spread of plant diseases, improving overall ecosystem health.
💡 Example! Some farmers grow pepper, bananas, or coffee alongside cardamom, boosting biodiversity and farm productivity! 🍌🌿☕
❌ The Negative Effects of Cardamom Farming on Biodiversity
⚠️ 1. Deforestation for Large-Scale Plantations
✔️ Some large-scale cardamom farms clear forests to expand production.
✔️ This leads to habitat loss for native plants and animals.
✔️ Soil degradation occurs when natural tree cover is removed.
💡 Warning! In some regions, intensive cardamom farming has led to the loss of native tree species, disrupting local ecosystems! 🌲🚜
⚠️ 2. Pesticide Use Harms Wildlife
✔️ Chemical pesticides kill beneficial insects, including pollinators.
✔️ Water contamination from runoff affects fish and amphibians.
✔️ Pesticides disrupt food chains, leading to population declines in birds and mammals.
💡 Sustainable Solution! Organic cardamom farming avoids harmful chemicals and encourages natural pest control instead! 🌿♻️
⚠️ 3. Soil Degradation & Loss of Microbial Diversity
✔️ Over-farming can strip soil of essential nutrients.
✔️ Excessive fertilizer use leads to poor soil health and loss of microorganisms.
✔️ Soil compaction can reduce underground biodiversity, affecting earthworms and fungi.
💡 How to Fix This? Farmers can use crop rotation, composting, and mulching to restore soil health! 🌾🌎
🌍 How to Make Cardamom Farming More Biodiversity-Friendly
✔️ Encourage shade-grown methods instead of clearing forests.
✔️ Use organic fertilizers and avoid chemical pesticides.
✔️ Plant multiple crops alongside cardamom to promote biodiversity.
✔️ Support fair-trade and organic farmers who prioritize sustainability.
✅ Final Thoughts: A Balance Between Farming & Nature
When done sustainably, cardamom farming can protect biodiversity while supporting local farmers. Choosing organic, shade-grown, and eco-friendly farming methods helps keep ecosystems thriving.